Lyme disease and autoimmune diseases can often be confused because both involve the immune system. Lyme disease is an infection caused by bacteria, while autoimmune diseases are conditions in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. One must look at how they differ and are alike to understand Lyme disease vs. Autoimmune disease.
Lyme and autoimmune diseases are two very different health conditions, and it is essential to understand their differences.
Lyme disease is caused by a bacterial infection, while autoimmune diseases are caused by an overactive immune system that attacks the body’s tissues.
Knowing the differences between Lyme disease and autoimmune disease can help you make informed decisions about your health and the health of your loved ones. This article will provide an overview of the differences between Lyme disease and autoimmune disease, so you can better understand the associated symptoms, treatments, and risks.

Overview Of Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is an infectious disease caused by bacteria called Borrelia burgdorferi. It is transmitted from one person to another by ticks. Other ways of transmission can occur, such as through blood transfusion or mother to baby during pregnancy.
Lyme disease is the most common tick-borne disease in the U.S., with an estimated 30,000 cases yearly.
While most cases occur in the Northeast, Midwest, and Pacific regions, cases have been reported in all 50 states. The CDC has reported that the number of cases has increased over the past few decades, likely due to increasing tick populations and migratory patterns.
Symptoms Of Lyme Disease
Early-stage Lyme disease usually has no symptoms or mild symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain, and headaches. Later-stage Lyme disease can cause more severe symptoms, including muscle aches, nerve pain, and heart problems.
If left untreated, the infection can travel to other body parts, including the heart, nerves, and muscles. These later stages of the disease can cause more severe symptoms, including headaches, paralysis, and even death.
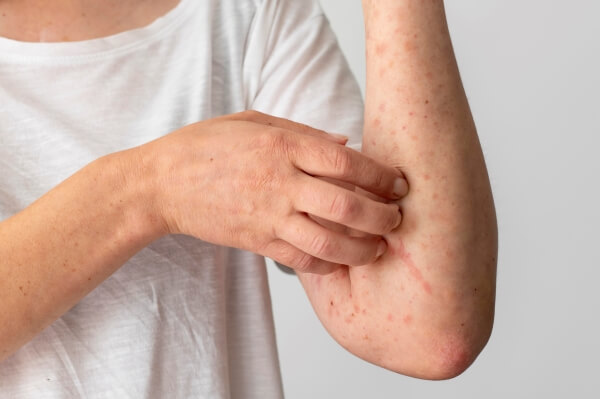
Rash On Your Skin
A rash on the skin is a common symptom of Lyme disease. This rash is often red and round and may have a bulls-eye appearance. It also may feel warm to the touch. This rash occurs when the bacteria from the tick bite travels to the skin, infecting it.
The rash may be painful and itchy, but it does not always appear.
If the rash does appear, it does not always indicate Lyme disease. It can also be caused by other infections such as brucellosis, Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia.

Joint And Muscle Pain
Joint pain and muscle aches are common in early-stage Lyme disease. If the infection spreads to the muscles and joints, you may experience more severe joint and muscle pain.
Lyme arthritis may occur if Lyme disease is left untreated. Lyme arthritis can cause swelling, joint pain, stiffness, and decreased flexibility. It usually occurs in the knees but may also affect other joints, such as elbows, wrists, ankles, and shoulders.

Headaches
Lyme disease triggers headaches in some people. The headaches can range from mild to severe and may last for days or weeks.
Headaches are a common symptom of Lyme disease. They are usually mild to moderate and may not respond to over-the-counter pain medications. Chronic Lyme disease may cause more severe headaches that can last for days or weeks.

Fatigue
Fatigue is another common symptom of Lyme disease. It may be mild at first, but as the infection progresses, it can become debilitating. Lyme disease fatigue differs from normal fatigue because it comes on suddenly and lasts longer than expected.
Treatments For Lyme Disease
If you think you have Lyme disease, it is essential to see your doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to curing the disease. The first step in treatment is getting tested. A blood test can determine if you have been infected. It is important to find a viable and reputable source of testing to determine if you have Lyme. Many cases are misdiagnosed due to potential inaccurate testing.
Your doctor may also recommend lifestyle changes, such as wearing bug spray outside and removing ticks as soon as possible when you find them.
Post-treatment Lyme disease includes fatigue, joint pain, and headaches that may not respond to medications. In these cases, your doctor may suggest lifestyle changes such as physical therapy, stress management, and improved sleep hygiene.
Overview Of Autoimmune Disease
An autoimmune disease occurs when your immune system mistakenly attacks your healthy body’s organs, tissues and cells. The immune system’s role is to naturally protect the body from infections and other harmful substances.
It identifies and fights off foreign invaders, such as bacteria and viruses, and repairs damaged cells and tissues. In autoimmune diseases, the immune system mistakenly identifies the body’s cells as foreign invaders and attacks them.
Other autoimmune diseases affect people of all ages, races, and ethnicities. Women are more likely to have autoimmune diseases than men.
Symptoms Of Autoimmune Disease
The autoimmune disease development process typically starts with a “trigger,” such as an infection or environmental toxin. This triggers the immune system to become active and attack the body’s cells and tissues. Here are some of the most common symptoms of autoimmune disease:
Arthritis And Joint Pain
Most autoimmune joint diseases cause inflammation and pain in the joints. The most common autoimmune joint disease is rheumatoid arthritis, which causes swelling and tenderness of the joints. Other autoimmune diseases that affect the joints include ankylosing spondylitis, lupus, gout, and psoriatic arthritis.
Inflammation And Fatigue
Chronic inflammation and fatigue are common symptoms of an autoimmune disorder. Inflammation occurs due to the immune system attacking the body’s cells and tissue.
Swollen lymph nodes, skin rashes, and fever may also occur due to inflammation. Fatigue is usually due to the body expending more energy than usual, fighting off the infection or foreign invader.
Skin Conditions
Some autoimmune diseases cause skin conditions, including psoriasis and dermatomyositis. The autoimmune response leads to skin rashes, lesions, and dryness.
Neurological Problems
Autoimmune diseases can cause neurological problems, including headaches, seizures, and other brain-related issues. Autoimmune diseases are often misdiagnosed, so it is essential to see your doctor if you think you have one. The sooner you are diagnosed, the sooner you can begin treatment to manage the disease.
Treatments For Autoimmune Diseases
There is no cure for autoimmune diseases, but treatments are available to help manage them. Depending on the type of autoimmune disease you have, your treatment plan may vary.
The goal of treatment is to reduce the symptoms and make it easier to manage the disease. Your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes, such as sticking to a healthy diet, getting plenty of sleep, and exercising.
Some autoimmune diseases can be treated with certain medications.
The adaptive immune system is designed to remember the foreign invader and defend against it if the body is exposed again. Lyme disease, however, does not fit this pattern.
Difference: Lyme Disease Is Caused By Bacteria
One of the significant differences between Lyme disease and autoimmune diseases is that Lyme infection is caused by a spirochete bacterium called Borrelia burgdorferi. People become infected when bitten by an infected tick carrying the bacteria.
The ticks can quickly spread Lyme disease if not removed properly from the exposure site. Lyme disease can cause many symptoms including fever, fatigue, muscle and joint pain, headaches, dizziness, and a characteristic skin rash.
Difference: Autoimmune Diseases Are Not Caused By Bacteria
Bacteria like Lyme disease do not cause autoimmune diseases. The condition develops when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in the body. There is no known cause for autoimmune diseases; however, genetics, environment, lifestyle, and other factors may contribute to their development.
Common autoimmune conditions include lupus, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), multiple sclerosis (MS), and type 1 diabetes. Symptoms vary from person to person depending on the type of autoimmune disease they have.
Similarity: Lyme Disease And Autoimmune Diseases Both Affect The Immune System
The similarity between Lyme disease and autoimmune diseases is that both involve the immune system. Lyme disease occurs when a person is infected with Borrelia burgdorferi, which triggers an immune response in the body. To fight off the infection, the immune system produces antibodies to attack the bacteria.
On the other hand, autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue rather than fighting off foreign invaders like bacteria or viruses. This leads to inflammation and destruction of vital organs or tissues in some cases.
Similarity: Lyme Disease And Autoimmune Diseases Have Similar Symptoms
The symptoms of Lyme disease and autoimmune diseases can also be similar. Common symptoms of Lyme disease include fever, fatigue, muscle and joint pain, headaches, dizziness, and a characteristic skin rash. Autoimmune diseases may cause fatigue, muscle aches, pains, shortness of breath, low-grade fevers, or rashes.
Conclusion
The differences between Lyme disease and autoimmune diseases are essential to accurately understand to manage any potential health issues that arise from either condition. Lyme disease is caused by a bacterial infection, while autoimmune diseases are not contagious and have no known single cause.
Both Lyme disease and some autoimmune conditions can affect the immune system and cause similar symptoms such as fatigue, muscle aches, and pains. Individuals need to seek medical advice to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment if they experience any of the above symptoms.